Lipoprotein(a): The Silent Heart Killer No One Talks About
Many people believe that if their cholesterol level is normal, their heart is safe. However, statistics show the opposite: heart attacks and strokes often occur in people whose test results do not raise any concerns.
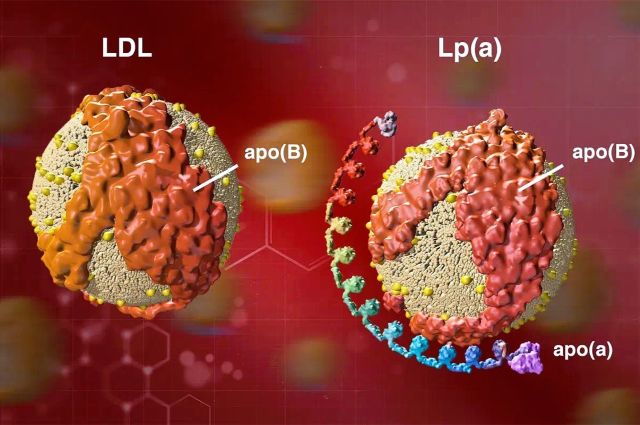
One of the reasons for such “unexplained” cases is lipoprotein(a) or Lp(a) - a little-known but extremely important marker of cardiovascular risk.









